![]() Click to go to back to the previous section
(Section 13.2)
Click to go to back to the previous section
(Section 13.2)
This section will take a look at several physiological measures of physical activity.
In the last several years, technology advances have made physiological measurement much easier and less expensive.
Devices such
as heart rate monitors, pedometers and accelerometers are smaller and more
robust making data collection on larger sample sizes possible.
Heart rate monitors
One of the first objective measures of physical activity consisted of heart rate monitoring.
The monitors, usually consisting of a chest strap and watch, are worn during physical activity by participants.
The monitors offer a convenient method for measuring a physiological indicator of the amount and intensity of physical activity.
The monitors display current heart rate but most models used in research store data for download at a later time.
From stored heart rate data, researchers can calculate time spent within specific heart rate ranges or above certain thresholds.
In controlled laboratory conditions, heart rate and measured VO2 have a linear relationship.
This relationship is strongest at the middle and upper thresholds of heart rate.
Therefore, researchers can estimate VO2 along with energy expenditure in their
subjects.
An advantage to heart rate monitors is the ability to have the subjects wear them just about anywhere and then download the data at a later time. The subjects are not restricted in their environment thus enabling their use for collecting physical activity data in the field or real-life settings.
Disadvantages to heart rate monitors include the initial cost of purchasing the
monitors and external factors that affect heart rate, such as stress and
environmental conditions (heat and humidity).
Motion sensors
Motion sensors can be divided into two main types, pedometers and accelerometers.
Pedometers are much less expensive and measure total physical activity by counting the number of steps an individual takes.
When walking is the predominant mode of physical activity, pedometers are quite effective as a measurement device.
Accelerometers are much more expensive, but provide more detailed information regarding intensity and direction of movement.
Accelerometer data can be downloaded and provides information on the patterns of time, duration and intensity of physical activity.
Certain accelerometers can be programmed with the participant’s age, height, weight and gender to estimate basal metabolic rate.
Additionally, total
energy expenditure can be estimated from the accelerometer counts.
The relative unobtrusiveness of motion sensors allow subjects to wear them in the field and throughout their daily lives.
The initial
cost of purchasing the motion sensors is a disadvantage just like heart rate
monitors, but the range of cost is greater depending on the complexity of the
sensor. Because data are collected using an objective method, they are usually
more reliable than subjective methods such as questionnaires and diaries.
Despite the sophistication of advanced motion sensors for measuring the duration and intensity of physical activity, not all activities can be measured.
Stationary biking, elliptical training, weight lifting, and any water based activity cannot be recorded with motion sensors.
Early researchers worried about the reliability of motion sensors when researching children.
They
worried that children would alter the counts by purposely jumping up and down or
taking off the sensor and shaking it. Later researchers have not seen these
behaviors in the children they were studying.
Calorimetry
Direct calorimetry involves the measurement of heat produced by the body during physical activity.
Only about 40% of the energy liberated during the metabolism of glucose and fats is used to produce ATP, and the remaining 60% is converted to heat.
A method to estimate the rate and quantity of energy production is to measure heat production.
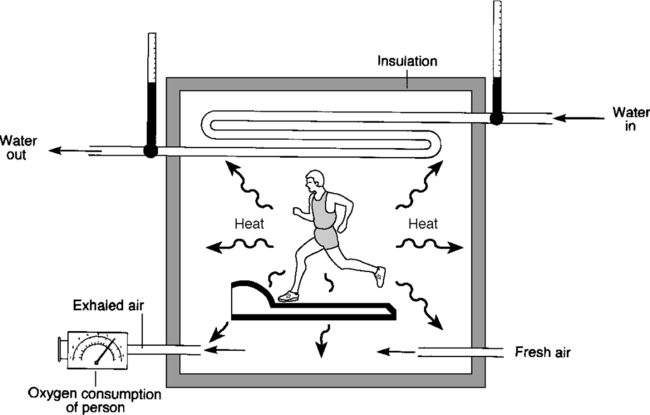
A calorimeter is an insulated, airtight chamber. A subject exercises in this chamber and the heat generated is transferred to the air and walls of the chamber.
This change in temperature is measured and metabolic rate can be
calculated.
Calorimeters are extremely expensive to construct and are slow to generate results.
he only real advantage is that they are a direct measure of heat produced. The measurements are extremely accurate for total energy expenditure; however, direct calorimetry cannot follow rapid changes in energy usage.
This method is seldom used today as it is easier and less
expensive to assess energy expenditure via indirect calorimetry.
Indirect calorimetry involves the measurement of respiratory gas exchange (oxygen consumption and carbon dioxide production) during a variety of controlled physical activities (cycle and treadmill exercise is common).
This is accomplished via open-circuit spirometry using relatively small gas analysis equipment or a metabolic cart.
The respiratory gas that is expelled by a subject passes through a hose into a mixing chamber, where the samples are pumped to electronic oxygen and carbon dioxide analyzers.
The computer recording equipment uses the measurements of respired gas volume and expired oxygen and carbon dioxide concentrations to calculate oxygen uptake and carbon dioxide production.
Although portable equipment does exist, most calorimetry procedures are still performed in the laboratory setting.
By measuring gas exchange (thus energy
expenditure) during specified modes of physical activity, the average energy
costs can be obtained for these activities.
The main advantage of indirect calorimetry is its extreme
accuracy. Therefore, indirect calorimetry is useful for compiling an activity
compendium and associated energy costs. There are numerous disadvantages to
indirect calorimetry:
·
High cost
·
Technical expertise necessary
·
Laboratory based measurement
·
Unsuitable for long-term measurement
Doubly labeled water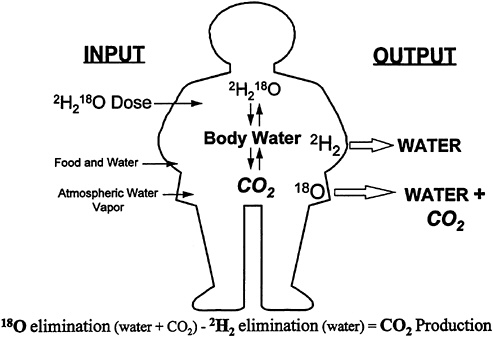
The doubly labeled water method can be used to measure total energy expenditure in unrestrained subjects for 1-4 weeks.
Procedures involve ingestion of a loading dose of water labeled with 2H and 18O.
2H is eliminated as water through urine, sweat, and water vapor.
18O is eliminated as both water and carbon dioxide through urine, sweat, water vapor and expired gas.
The difference between the two elimination rates is a measure of carbon dioxide production.
By collecting urine, blood, or saliva at regular intervals, elimination levels can be monitored and calculations of carbon dioxide production can be used to estimate total energy expenditure.
Samples are
collected at baseline then at regular intervals until final measurement at 1 to
4 weeks, depending on specific protocol.
Doubly labeled water is currently the most accurate way to measure total energy expenditure and is considered the gold standard. Often it is the criterion measure that new measurement techniques are judged against.
Because of the expense of the doubly labeled water method, only small populations are usually feasible without a large research grant or other funding source.
The price of the test
includes the initial dose of doubly labeled water and the processing and
subsequent laboratory testing of the samples.
Summary
The measurement of physical activity is important because of the established connection between physical activity and mortality/morbidity.
Rapid technology advances over the past few years has dramatically changed research methods and this trend will probably continue as measurement devices become smaller and more accurate.
The method of choice for physical activity assessment is a function of several factors, such as study size, population characteristics, ease of administration and cost.
Researchers are encouraged to use instruments that have been thoroughly evaluated and are considered reliable and valid.
When a new method is developed, the researcher should evaluate the
new method against a gold standard.
You have reached the end of Topic 13.
You must complete the review quiz before you can advance to the next topic.